Introduction
Increasingly complex food chains struggle to guarantee safe food supplies, particularly for a growing and vulnerable global population [1]. Alarmingly, foodborne outbreaks continue to threaten public health, with over 1,000 cases reported in the Netherlands alone in 2022 [5], underscoring the need for stronger solutions. While quality standards like GMP and HACCP are common, their effectiveness varies [4]. Additionally, declining consumer trust demands greater transparency [9].
Can Big Data, IoT, Blockchain, and advanced analytics revolutionize food safety and boost consumers’ trust in the food industry? This article explores this potential, drawing on the findings of a project with QAssurance that researched the impact of digital technologies on food safety.
Why Consumers Doubt the Food Industry
Consumer trust in the food industry is eroding due to several factors: lack of transparency [9], concerns about sustainability [6], and quality/safety issues [6] (Figure 1). Growing misinformation further fuels this mistrust (US).
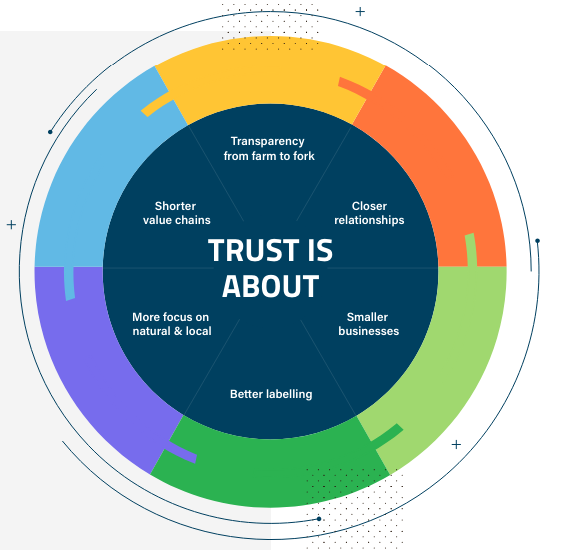
Key Technologies for Food Safety and Trust
Digital technologies are all electronic tools, devices, and systems that use digital information to create, store, manage, and transmit data. According to the EIT, digital technologies will be trends in the food industry in 2024 [8]. Examples of digital technologies that are being increasingly adopted in the food industry include [3]:
- Big Data – large, complex data sets (e.g., food safety database records, data from sensors, multimedia content)
- Internet of Things (IoT) – a network of connected physical devices that care to share data (e.g. sensors, embedded devices)
- Blockchain – a tamper-proof shared record-keeping system
- (Big) Data analytics – innovative analytics transforming raw information into actionable insights for better decision-making. (e.g., Machine Learning, AI)
-> Digital technologies are fueling a more proactive approach to food safety thanks to [2]:
- Real-time data: Big Data and IoT devices capture information throughout the food chain
- Secure data recording: By ensuring the integrity of collected data, they enable reliable analysis and informed decision-making
- Advanced data analytics: Innovative techniques identify patterns and trends allowing for targeted interventions and risk mitigation strategies.
Understanding Consumers Take on Digital Tools
Digital tools promise to revolutionize food safety, but consumer trust in the industry remains low [8]. Since consumer preferences drive change, neglecting these concerns could stall progress. Can digital tools not only enhance safety but also rebuild trust?
To explore consumers’ behaviour, a survey conducted within a QAssurance project on investigating the impact of digital tools on food safety, aimed to assess their trust in the food industry and then introduced the concept of digital tools for food safety management. Read on to discover the survey’s findings.
The Broken Trust
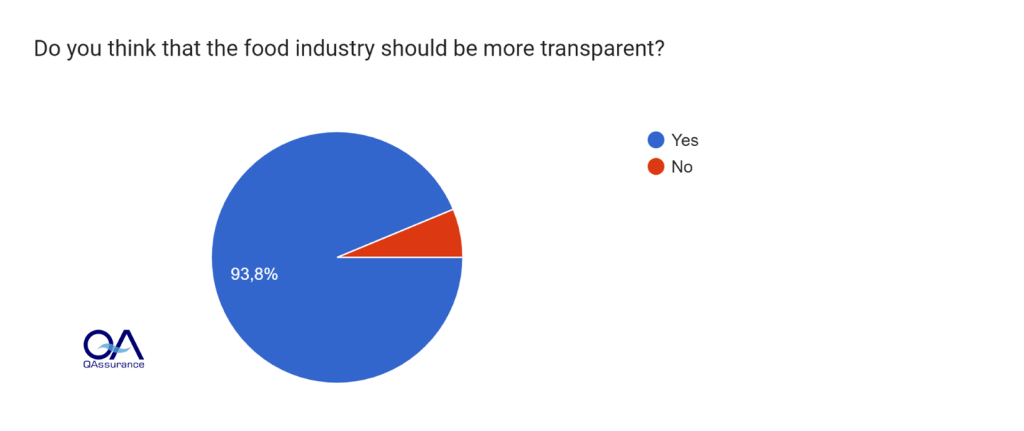
Building on the earlier discussion of declining consumer trust, the survey revealed that:
- A strong majority (59%) of consumers expressed distrust in the food industry, while a staggering 94% desired greater transparency (Figure 2)
- In fact, transparency topped consumer concerns when buying food products, with 78% worried about false packaging information and undeclared ingredients
Consumers Perception and Trust of Digital Tools in Food Safety
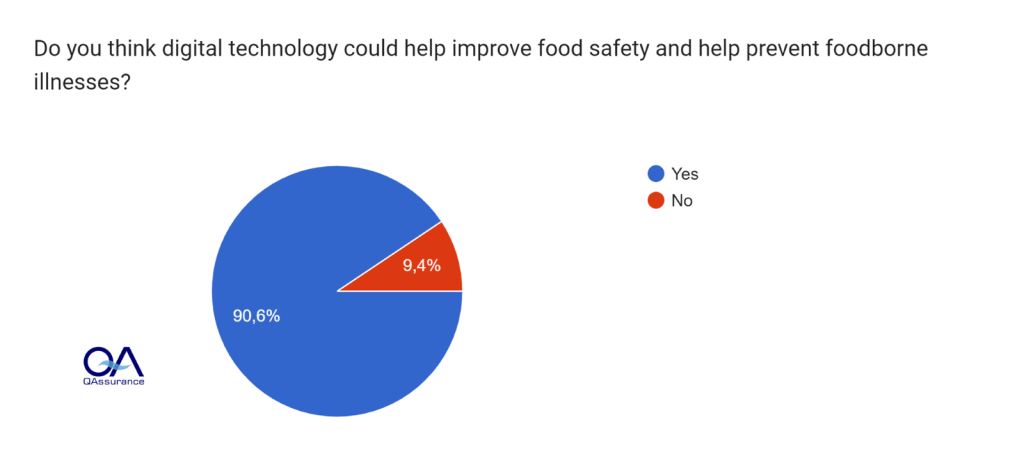
Consumer awareness of digital tools was explored in the survey as well, together with their perception of them:
- While most consumers use digital solutions to buy food and find nutritional information (53%), they remain largely unaware of the potential these tools hold for food safety management
- However, a strong majority (91%) of consumers believe digital tools can improve food safety and prevent foodborne illness (Figure 3)
- This potential for improved safety also translates to trust, with 81% indicating that it could improve their trust in the food industry
The Trust Gap: Consumers Skepticism
While consumers see promise in digital tools, some concerns remain. The survey delved into these concerns, revealing that:
- Reliability of digital tools topped consumer concerns (78%), followed by job displacement due to automation (53%).
- Data privacy emerged as another concern, with 66% of consumers fearing companies might misuse digital tools for data collection.
iMIS Food – Real-Time Food Safety Compliance
iMIS Food platform empowers food businesses to manage food safety with confidence. Validated over 1000 times, it supports compliance (EU & GFSI) with a user-friendly QMS and the promotion of continuous improvement. The iMIS Food Compliance portal keeps you informed of food safety issues, ensuring real-time food assurance for the future, fostering transparency and therefore also improving your relationship with customers and consumers.
Digital Revolution : Are you ready?
The food industry is changing, and the way food safety is managed is evolving, but are you and your company ready for this change?
Take the test to see if you are ready for a better change, with the “Digital Transformation Calculator” and explore digital solutions for food safety management:
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital technologies are increasingly revolutionizing the food industry and their adoption could potentially:
- Improving prevention and resolution of food safety incidents
- Improving traceability and food fraud prevention
- Boosting consumer trust
-> However, to unlock the full potential of digital tools and rebuild consumer trust, addressing their concerns is crucial.
Sources
- [1] FAO. (2023a). Thinking about the future of food safety. In Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. https://www.fao.org/3/cb8667en/cb8667en.pdf
- [2] FAO. (2023b). Early warning tools and systems for emerging issues in food safety – Technical background. In FAO eBooks. https://doi.org/10.4060/cc9162en
- [3] Food Standards Agency. (2021). Emerging technologies that will impact the UK Food System
- [4] Luning, PA. & Wageningen University and Research. (2011). Tools to support the self-assessment of the performance of Food Safety Management Systems. https://edepot.wur.nl/175678
- [5] Number of reported illnesses related to food consumption increases each year | RIVM. (n.d.). https://www.rivm.nl/en/news/number-of-reported-illnesses-related-to-food-consumption-increases-each-year
- [6] Stiff, R. (2022, March 10). Consumer trust in the food industry has declined in the past year. How can we change that? U.S. Farmers & Ranchers in Action. https://usfarmersandranchers.org/stories/food-trends-culture/consumer-trust-in-the-food-industry-has-declined-in-the-past-year-how-can-we-change-that/
- [7] Top 5 food trends in 2024 – EIT Food. (n.d.). EIT Food. https://www.eitfood.eu/blog/top-5-food-trends-in-2024#:~:text=The%205%20top%20food%20trends,of%20regenerative%20agriculture%20will%20emerge
- [8] What is the state of consumer trust in the European agrifood industry? – EIT Food. (n.d.). EIT Food. https://www.eitfood.eu/blog/what-is-the-state-of-consumer-trust-in-the-european-agrifood-industry
Related articles to Tech and Big Data: Improving Trust in the Food Industry
Many customers and visitors to this page 'Tech and Big Data: Improving Trust in the Food Industry' also viewed the articles and manuals listed below:
